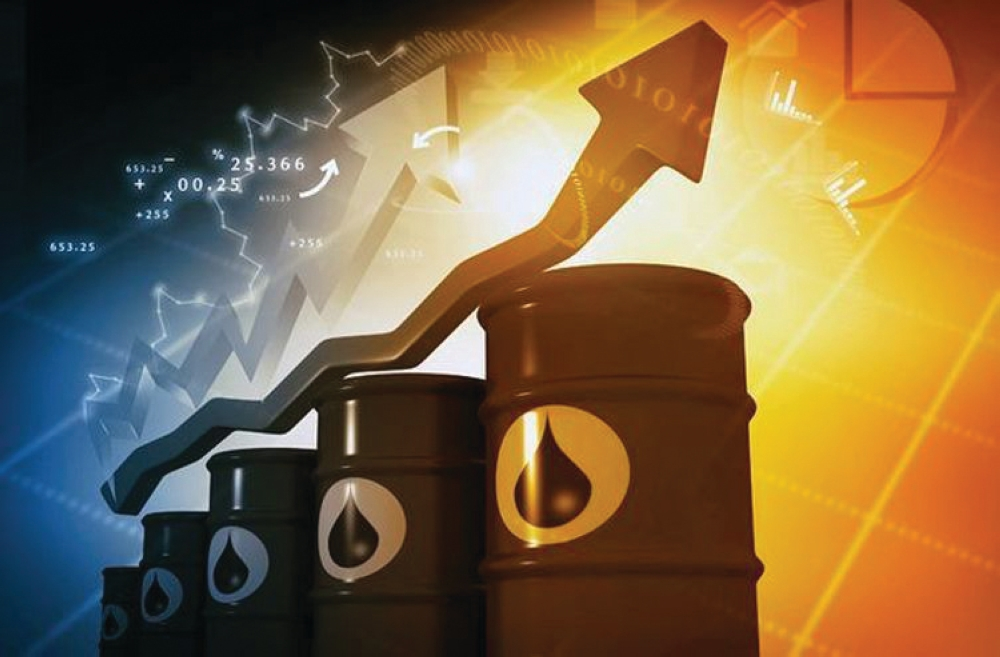
Global oil prices surged at the close of trading on Thursday, rising by more than 3%, a move reflecting the market's extreme sensitivity to geopolitical factors and indicators of global demand. This increase underscores the volatility prevailing in energy markets amidst complex economic and political variables.
In more detail, Brent crude futures rose by $2.31, or 3.38%, to settle at $70.71 a barrel. Meanwhile, West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude futures also saw a significant increase of $2.21, or 3.5%, closing at $65.42 a barrel.
Background and context of oil price fluctuations
Historically, oil markets have been among the most sensitive financial markets to global events. The price of a barrel of oil is directly affected by a delicate balance between supply and demand. Any disruption to this balance, whether real or perceived, leads to sharp price movements. Factors affecting the supply side include decisions by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies (OPEC+) regarding production levels, as well as any geopolitical tensions in key oil-producing regions such as the Middle East, which could threaten to disrupt supplies.
On the demand side, the health of the global economy plays the most significant role. Strong economic growth in major consuming countries, such as China and the United States, means increased industrial activity and transportation, thus increasing energy demand and driving prices up.
The significance and expected effects of the recent rise
The rise in oil prices has far-reaching implications both regionally and internationally. For oil-exporting countries, particularly in the Gulf region, this increase represents a significant boost to their public revenues, helping to strengthen their budgets and finance development projects. However, for importing countries, the higher cost of energy poses a major challenge, leading to increased import bills and potentially fueling inflationary pressures, thus impacting consumer purchasing power and raising production costs for businesses.
At the international level, the continued rise in energy prices could influence the policies of global central banks, which may be forced to tighten monetary policy to curb inflation. Therefore, investors and policymakers closely monitor oil price movements as a vital indicator of the health and future direction of the global economy.